Principles of Anti-corrosion
-
-
It is desirable to consider the anti-corrosion method from the design stage of the structure, sufficiently taking into consideration the type and shape of the metal, purpose of use, environmental conditions, anti-corrosion period, and economic feasibility. Since wet corrosion generally occurs more frequently, if water and oxygen are not present, there will be no generation of local battery, and corrosion will not occur. Therefore, preventing the metal surface from corrosion by blocking water and oxygen is called anti-corrosion. The primary goal of the anti-corrosion method by coating is to block corrosion factors (water, oxygen, acid, salt) by forming a film. Most paints are capable of alleviating corrosion through interception of the corrosion factors to some extent by forming a coating film. However, it is difficult to expect a long-term anti-corrosive effect.
Therefore, paints made by using various anti-corrosive pigments and resins to which penetration of corrosion factors is difficult in order to prevent corrosion of the metal are called anti-corrosive paints (rust preventive paints). Therefore, anti-corrosion principles can be classified according to which anti-corrosion pigment is used for the paint. The classification is as follows.Principles of Anti-corrosion
1. Cathodic Protection Method (Self-sacrifice Method)
Corrosion of iron is carried out by the movement of electrons. The cathodic protection method is to delay the corrosion of iron as much as possible by containing a large amount of pigment with a higher ionization tendency than iron in the paint and making it corroded first.
① Typical pigment with the cathodic protection method
ZINC POWDER ② Typical Product
Inorganic Ethyl Silicate Primer DHDC-1800
Inorganic Ethyl Silicate Shop Primer DHDC-1650
Epoxy Zinc Rich Primer DHDC-1610
Epoxy Zinc Rich Primer High Build DHDC-1610HB2. Reaction Inhibition Effect
A method of delaying or preventing corrosion of iron by reacting with harmful elements (water, oxygen) in advance by adding a chemically active pigment, namely passivation of iron.
① Typical pigment with a reaction inhibition effect
RED LEAD, ZINC PHOSPHATE, ZINC CHROMATE ② Typical product (examples of epoxy anti-corrosive primer)
Zinc phosphate epoxy anti-corrosive primer DHDC-0690ZP
Zinc chromate epoxy anti-corrosive primer DHDC-0690ZC
Red lead epoxy anti-corrosive primer DHDC-0690RL3. Blocking Effect
A method of preventing the corrosion of iron by blocking the penetration of harmful elements by adding a pigment with a structure to which the penetration of harmful elements is difficult.
.
① Typical pigment with a blocking effect
MIO (Micaceous Iron Oxide), GLASS FLAKE, Aluminum ② Typical product
Epoxy MIO (silver gray) DHDC-6000MIO
Chlorinated Rubber MIO (silver gray) DHDC-4000MIO
Phenol MIO (silver gray) DHDC-2000MIO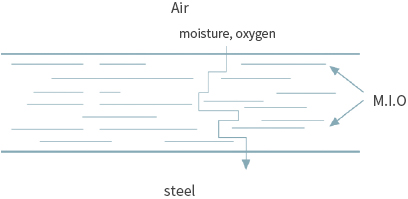
4. Iron Oxide Anti-rust Effect
A method of preventing the corrosion of steel by forming a stable iron oxide film on the steel by adding chemically stable oxide to paint
① Typical pigment
IRON OXIDE RED ② Typical product (examples of epoxy anti-corrosive primer)
Iron Oxide Epoxy Anti-corrosive Primer DHDC-0690
Iron Oxide Epoxy Anti-corrosive Primer DNY-130
Quick-drying Epoxy Anti-corrosive Primer Speed Poxy 100
-